Targeted Genome Fragmentation with CRISPR/Cas9 Enables Fast and Efficient Enrichment of Small Genomic Regions and Ultra-Accurate Sequencing with Low DNA Input (CRISPR-DS)
Enhancing the Accuracy of Next-Generation Sequencing for Detecting Rare and Subclonal Mutations

Next-generation DNA sequencing promises to revolutionize clinical medicine and basic research. However, while this technology has the capacity to generate hundreds of billions of nucleotides of DNA sequence in a single experiment, the error rate of ∼1% results in hundreds of millions of sequencing mistakes. These scattered errors can be tolerated in some applications but […]
Sequencing small genomic targets with high efficiency and extreme accuracy
Detecting Ultralow-Frequency Mutations by Duplex Sequencing
Detection of Ultra-Rare Mutations by Next-Generation Sequencing
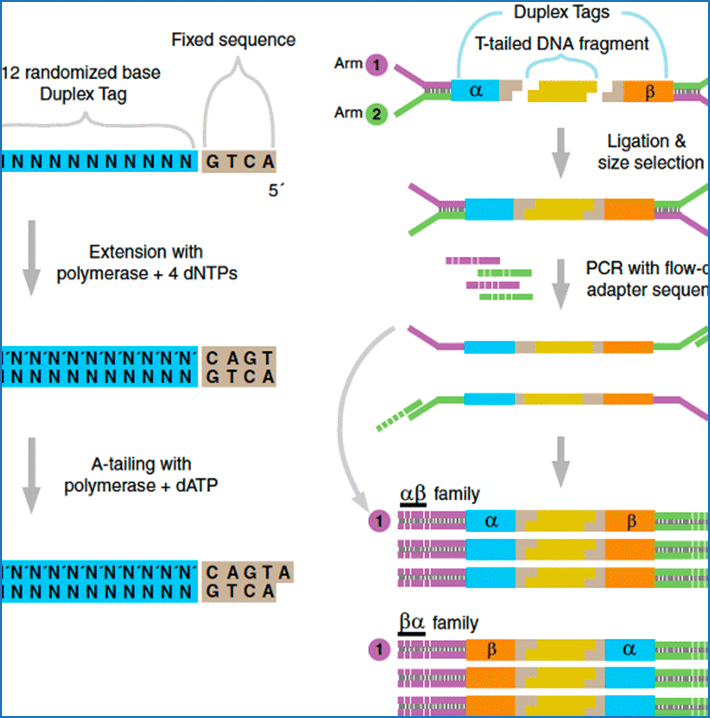
Mutations, the fuel of evolution, are first manifested as rare DNA changes within a population of cells. Although next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies have revolutionized the study of genomic variation between species and individual organisms, most have limited ability to accurately detect and quantify rare variants among the different genome copies in heterogeneous mixtures of cells […]
